Why We Need Nagios?
- Detects all types of network or server issues
- Helps you to find the root cause of the problem which allows you to get the permanent solution to the problem
- Active monitoring of your entire infrastructure and business processes
- Allows you to monitors and troubleshoot server performance issues
- Helps you to plan for infrastructure upgrades before outdated systems create failures
- You can maintain the security and availability of the service
- Automatically fix problems in a panic situation
History of Nagios
Features of Nagios
- Relatively scalable, Manageable, and Secure
- Good log and database system
- Informative and attractive web interfaces
- Automatically send alerts if condition changes
- If the services are running fine, then there is no need to do check that host is an alive
- Helps you to detect network errors or server crashes
- You can troubleshoot the performance issues of the server.
- The issues, if any, can be fixed automatically as they are identified during the monitoring process
- You can monitor the entire business process and IT infrastructure with a single pass
- The product's architecture is easy writing new plugins in the language of your choice
- Nagios allows you to read its configuration from an entire directory which helps you to decide how to define individual files
- Utilizes topology to determine dependencies
- Monitor network services like HTTP, SMTP, HTTP, SNMP, FTP, SSH, POP, etc.
- Helps you to define network host hierarchy using parent hosts
- Ability to define event handlers which runs during service or host events for proactive problem resolution
- Support for implementing redundant monitoring hosts
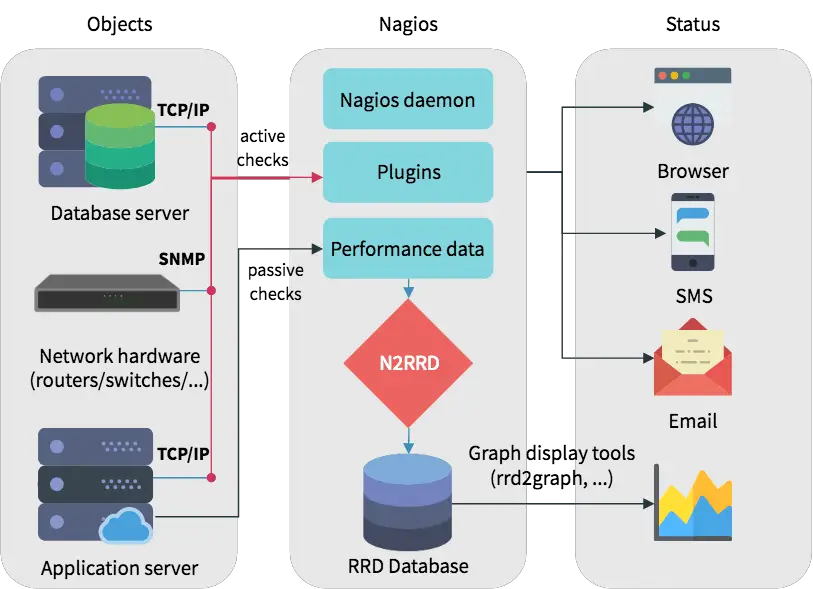
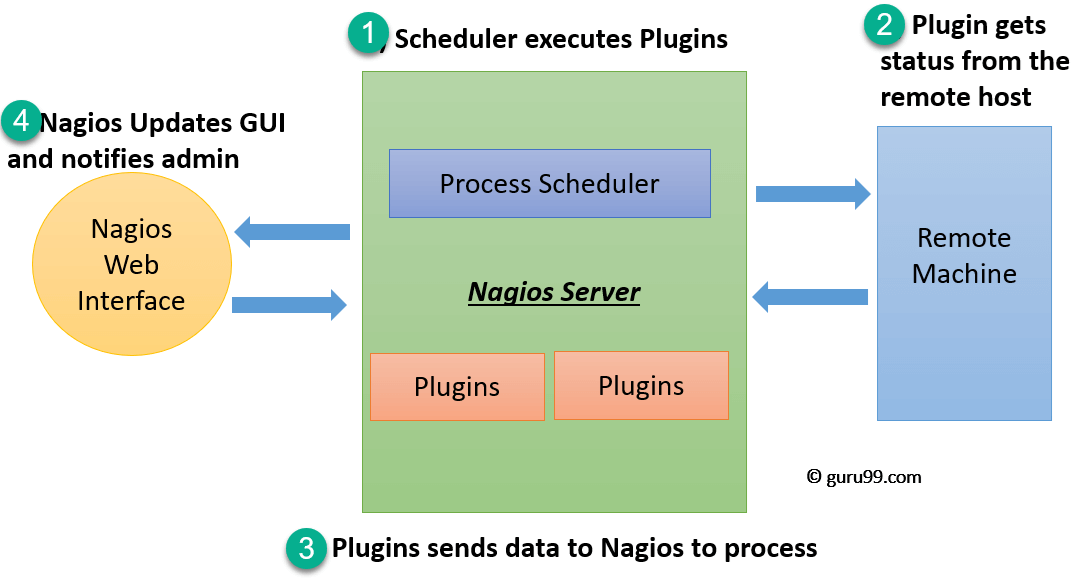
Nagios Architecture
- The scheduler is a component of server part of Nagios. It sends a signal to execute the plugins at the remote host.
- The plugin gets the status from the remote host
- The plugin sends the data to the process scheduler
- The process scheduler updates the GUI and notifications are sent to admins
- Check_nt is a plugin to monitor a windows machine which is mostly available in the monitoring server
- NSClinet++ should be installed in every Windows machine that you wants to monitor
- There is an SSL connection between the server and the host which continuously exchange information with each other

Get practical working on Nagios from live experts at DevOps Online Course
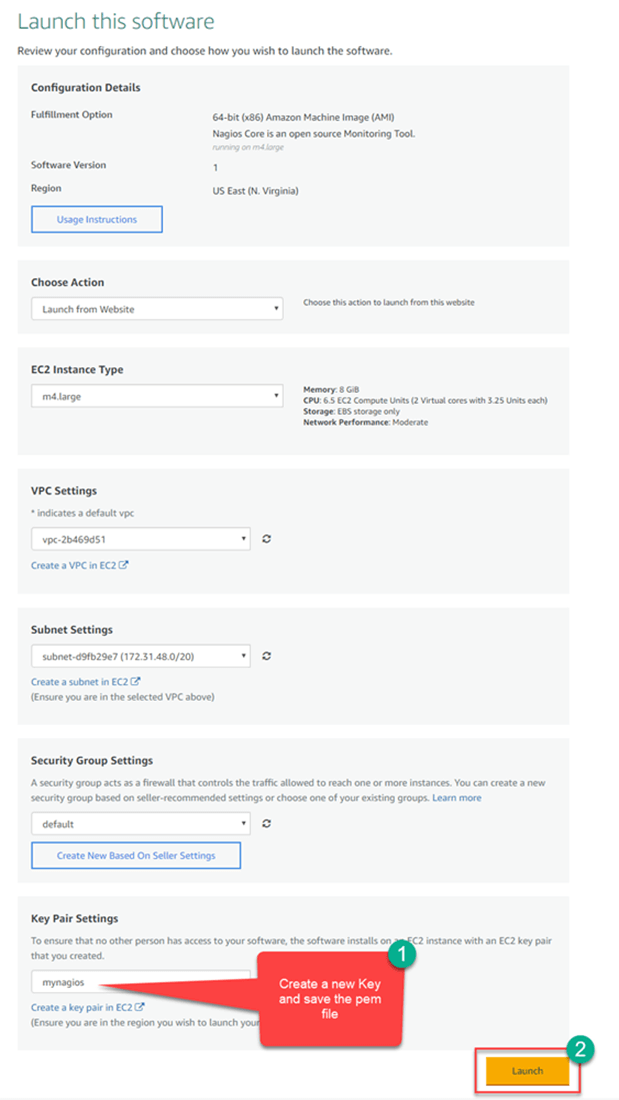
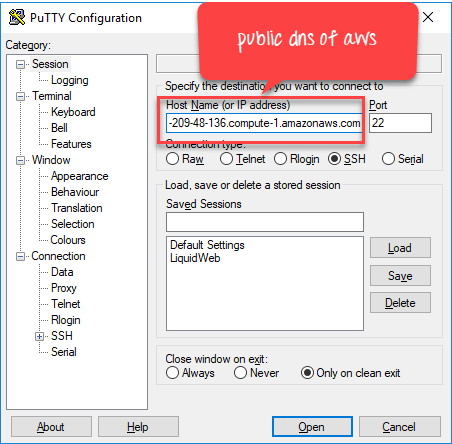
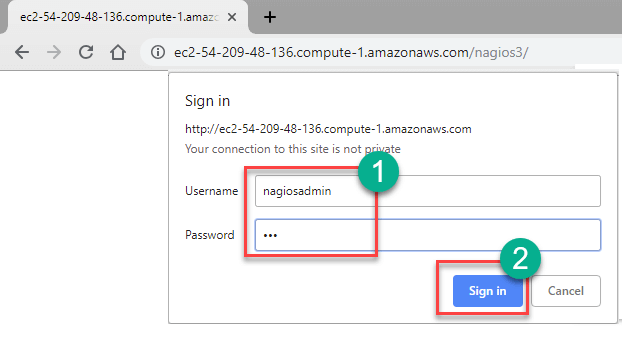
Install Nagios at AWS
- Enter login name as ubuntu
- Run this command sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nagios3/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
- Enter a new password of your choice
Application of Nagios
- Server & Network Nodes
- Application monitoring from a single console
- Application Monitoring with transaction-level insights
- Monitor Middleware & Messaging Components
- Customizable Reports and Dashboards
- UPS Backup System
- Bio-Metric Identification System
- Temperature & Humidity Control System (Sensing Mechanism)
- CCTV/NVR System
- Storage Subsystem (NAS&SAN)
Disadvantages of Using Nagios
- Important feature like wizards or interactive dashboard are only available on Nagios XI, which is quite an expensive tool
- Nagios core has a confusing interface
- There're many configuration files which are very hard to configure for users
- Nagios can't monitor network throughput
- The tool not allows you to manage the network but only allows to monitor the network
- Nagios makes no difference between various devices like servers, routers, or switches as it treats every device as a host